Arthritis is a general term used to describe a variety of conditions that generally damage the joints and its surrounding tissues. The severity depends on lifestyle and can range from mild to severe. It is common in adults aged 65 and over but can also affect people of all ages.
Research to date has not found any cure for arthritis but there are ways to manage the symptoms.
There are many different types of arthritis but in this article, we will focus on the three most common types of arthritis, namely, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis & Gout.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a common condition that involves inflammation and pain of the joints and the structures that surround it, which includes cartilage, ligaments, and muscles. Osteoarthritis is when the cushion, ‘cartilage’ between the joints starts to wear away causing the bones to rub against each other, this process is commonly known as “wear and tear”.
Typical Symptoms Of Osteoarthritis
- Pain
- Stiffness and swelling
- Decreased range of movement
Some key characteristics of Osteoarthritis are cartilage damage, joint inflammation and bony growths, ‘osteophytes’ around the affected area.
Those At Risk Of Osteoarthritis
- Elderly
- People with a family history
- Overweight people
- People performing repetitive movements
- People with previous injuries
If this condition is left untreated Osteoarthritis will progressively get worse over time.
Diet & Lifestyle Preventative Measures For Osteoarthritis
Things that we can do to help manage the symptoms of mild to moderate Osteoarthritis are to stay active, maintain a healthy weight and seek assistance with addressing the cause of aches and pains before they become chronic problems.
Beyond that, natural supplements such as glucosamine/chondroitin & fish oils have been shown to slow down the progression of osteoarthritis and also assist with reduction of symptoms.
Medical Treatments For Osteoarthritis
Medications that may help relieve osteoarthritis symptoms may include:
Acetaminophen, has been shown to help some people with osteoarthritis who have mild to moderate pain.
Taking more than the recommended dose of acetaminophen can cause liver damage.
Over-the-counter NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, paracetamol and naproxen, taken at the recommended doses, typically relieve osteoarthritis pain. NSAIDs can cause stomach upset, cardiovascular problems, bleeding problems, and liver and kidney damage. NSAIDs as gels, applied to the skin over the affected joint, have fewer side effects and may relieve pain just as well.
Duloxetine (Cymbalta), normally used as an antidepressant, is also approved to treat chronic pain, including osteoarthritis pain.
If pain is still persistent there are other surgical/medical treatments including:
- Cortisone injections which may relieve pain in the joint through decreasing inflammation with injected corticosteroid medication.The number of cortisone injections you can receive each year is generally limited to three or four injections because the medication can aggravate joint damage over time.
- Injections of ‘lubricants’, hyaluronic acid may offer pain relief by providing some cushioning in your knee, though some research suggests these injections offer no more relief than a placebo.Hyaluronic acid is similar to a component normally found in your joint fluid, ‘synovial fluid’.
- If osteoarthritis has damaged one side of your knee more than the other, an osteotomy might be helpful. In a knee osteotomy, a surgeon cuts across the bone either above or below the knee, and then adds or removes a wedge of bone. This shifts your body weight away from the worn-out part of your knee joint.
- Joint replacement (arthroplasty), your surgeon removes your damaged joint surfaces and replaces them with plastic and metal parts. Surgical risks include infections and blood clots. Artificial joints can wear out or come loose and may need to eventually be replaced.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
This type of arthritis is classified as an autoimmune disease due to the immune system not functioning correctly and attacking its own body.
When first experiencing these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible as it is possible to have permanent damage from rheumatoid arthritis.
Typical Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Pain
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Impaired joint function
- Redness
- Deformities of the bone structure
- Often rheumatoid arthritis affects both sides of the body, meaning if you have the condition somewhere on your right side, your left side will also develop rheumatoid arthritis in a similar location soon after.
- If you are suspected to suffer from rheumatoid arthritis, then your general practitioner will recommend you go see a rheumatologist.
Those At Risk Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
It is uncertain what causes the body’s immune system to attack its own cells, but research suggests there are some factors that may contribute to the development of rheumatoid arthritis:
- Middle-aged people, rheumatoid arthritis can affect any age group but typically it affects those between the ages of 40-60.
- More so females than males, Females are three times more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis than men.
- Those in unique environments with poor air quality, or exposure to bacteria & viruses
- Family History- you may have a higher chance of developing rheumatoid arthritis if you or a member of your family have the genetic marker HLD-DRB1. Studies have also shown that some families of people who have the genetic marker HDL never developed Rheumatoid arthritis and those who do not have it at all can develop it.
Diet & Lifestyle Preventative Measures For Rheumatoid Arthritis
With rheumatoid arthritis, early detection is critical in slowing and maintaining healthy joint function before any further permanent damage is incurred.
Adjusting certain lifestyle factors is important to slow down the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Below is a list that can help manage rheumatoid arthritis:
- Gentle exercise
- Rest (During a flare-up)
- Hot and cold therapy
- Diet high in anti-inflammatory content including:
- Tomatoes
- Olive oil
- Green leafy vegetables, such as spinach, kale, and collards
- Nuts like almonds and walnuts.
- Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines.
- Fruits such as strawberries, blueberries, cherries, and oranges.
Medical Treatments For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Below are some types of medications that can help manage rheumatoid arthritis.
- Corticosteroids
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
- Janis kinase inhibitors (JAK)
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Acetaminophen)
Gout
A type of arthritis that mainly affects the joints of the body. This condition is due to a build-up of uric acid that is lodged in the joints making it feel like being stabbed by a hot rod.
Purine is normally broken down within the body forming uric acid which is excreted through urine. Gout occurs when there is a build of up of these uric acids in the bloodstream due to the kidneys not functioning well enough to remove them. The uric acid accumulates to the point that it forms crystal-like objects which are lodged in joints, usually starting with the big toe causing pain, swelling and loss of function.
It is important to have gout sorted out as quickly as possible, allowing the condition to linger may cause permanent damage to the joints.
Typical Symptoms Of Gout
There are no warning signs of gout, it comes on very fast and usually affects a very specific joint. Signs and symptoms of gout are:
- Sharp stabbing pain of a very particular joint (usually the big toe)
- Redness
- Swelling
- Pain can last anywhere between 1 to 14 days (Depending on how it is managed)
Those At Risk Of Gout
Gout was commonly known as “the rich man’s disease”, since in the past, only the rich could afford luxurious food such as meat and alcohol. This type of arthritis is more common in men than women and mainly targets the elderly, but gout can also occur at middle age as well.
Certain foods and medication may increase the chances of gout, these are:
- Diuretic medication
- Overweight
- A diet consisting of red meats, alcohol, shellfish, animal organs such as liver
- Those with a family history
Diet & Lifestyle Preventative Measures For Gout
Although gout may come on suddenly, below are a list of methods to help manage gout:
- Avoid food high in purines such as shellfish, organs, red meat, and alcohol.
- Keep hydrated and drink plenty of water.
- Exercise often and adjust the type of training that doesn’t utilize the affected joint.
Medical Treatments For Gout
Generally, a GP is able to diagnose gout, other methods of gout detection are either an x-ray or a sample fluid at the affected joint. There are medications specifically designed to help manage and prevent gout, but for long-lasting results, a strict lifestyle change must be applied to be able to manage pain and improve organ function.
Pharmaceutical drugs used to treat symptoms of Gout include:
- Anti-inflammatory medications such as Ibuprofen, colchicine or corticosteroids.
- Allopurinol a drug that can either be taken orally or injected to help with the prevention of gout.
Natural Treatments That Work!
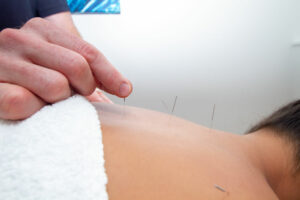
Arthritis is a common presentation and is frequently dealt with. A variety of powerful, natural treatment techniques may be used to assist in the management of arthritis which may include acupuncture, moxibustion, cupping, and lifestyle modifications.
Acupuncture
Helps promote the circulation of the entire body. This treatment targets specific areas such as inflamed and painful joints. Acupuncture needles are inserted into specific points on the body which stimulates nerves to release our body’s own natural pain killers (endorphins) and anti-inflammatory (cortisol). This, in turn, helps manage pain and inflammation that is present with arthritis.
Cupping Therapy
This form of therapy aids in the removal of toxic waste and build-up of fluid (oedema) which allows the body to function more optimally, thus help reduce inflammation within the muscles, tendons and joints.
Moxibustion
This type of therapy involves the burning of a moxibustion (moxa) stick. It is a gentle heat therapy that helps manage a wide variety of pain conditions. Burning moxibustion sticks gives off minimal smoke and is placed above the skin with no contact. Similar to Acupuncture, moxa sticks utilise Acupuncture points along the body or near the affected area. The therapy radiates a light heat sensation that helps dilate blood vessels, which promotes healing by stimulating blood circulation and reduction of stiffness.

Professional Guidance
Although all these modalities can help with the management of arthritis, it is important to consult with your health practitioner to find out what is most relevant for your situation. Sometimes it is more appropriate to use one therapy over another depending on what the situation is.