The back is fundamental to our structure; it holds us upright, connects and stabilises us by withstanding a massive amount of forces daily. Additionally, the back also contains various nerves and vessels that send and receive electrical signals and multiple substances to/from other areas of the body.
Due to the forces placed on the back and its unique composition, it is no wonder why back pain is a widespread symptom.
What Causes Back Pain?
The back is made up of various tissues; each has its role in providing structure, stability, and transmitting electrical signals/substances.
Each one of these tissues is prone to injury from various stressors, which may include:
- Everyday activities such as mowing the lawn, working at a computer, or merely sitting/sleeping awkwardly on the lounge.
- Traumatic incidents, including sporting injuries, car crashes, or falls.
In addition to this, some types of back pain may relate to systemic Illnesses/organ dysfunction such as anxiety, heart attack, pneumonia or kidney stones.
There are various causes of back pain. To accurately diagnosis, it is best to consult with your healthcare professional.
Through understanding causative factors, it is possible to implement changes in lifestyle/treatment to reduce or even resolve back pain altogether.
When To See A Health Professional For Back Pain

In general, most back pain will get better over time or with some form of self-care over several weeks. If, however, your back pain is:
- From a traumatic incident
- Painful with an inability to move
- Accompanied by unexplained weight loss, fever or changes in bowel movements
It is recommended to see a healthcare professional or call for emergency services.
Upper Back Pain
The upper and mid back consists of 12 spinal segments called thoracic vertebrae. You may hear your doctor referring to them as T1 to T12.
The upper and mid back is designed not only to connect our head to our hips, but to protect the vital organs such as our lungs and heart through their connection with the ribcage.
Upper back pain may lead to:
- Headaches
- Neck tension
- Shoulder immobility
- Breathing difficulty
- General aches and pain in the upper half of the body.
Causative factors of upper back pain may include:
- Long office hours
- Spinal misalignment
- Excessive coughing
- Incorrect posture
- Poor sleep habits
- Imbalanced muscle tone
- Anxiety/Stress
- Injury
- Pre-menstrual tension
Lower Back Pain
The lower back continues off from the upper back and contains what is known as the lumbar vertebrae. We have 5 of them and doctors will refer to this region as L1 to L5. The importance of the lumbar spine is to support the weight of the torso, upper limbs and head; it allows us to bend back and forth, protects the spinal cord, and helps absorb shock from activities such as jumping or bearing weight.
What Can Lower Back Pain Lead To?
Lower back pain may cause some physiological changes to the body, such as:
- Changes in walking style
- Postural changes
- Reduced mobility and strength
- Emotional distress
Causative Factors
Causes of lower back pain are like upper back pain but can also include:
- Obesity
- Arthritis
- Acute cauda equina syndrome (spinal cord injury)
- Osteoporosis
Back Pain Treatment
Back pain can have a significant impact on the quality of life, leaving sufferers disabled and emotionally challenged.
However, did you know most back pain, even severe back pain, improves by itself within six weeks? It is essential to consider what treatment can help speed up this recovery process and also will there be any side effects? Surgery is generally only considered if other therapies outlined below are not sufficient.
For acute back pain, heat packs and adjusted physical activities may be all that is needed. Continue light activities as much as you can and stop activities that increase pain.
Medications
Depending on the type of pain you are experiencing, a doctor might recommend the following:
Over The Counter (OTC) Pain Relievers
OTCs include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), such as Panadol and Nurofen. These may be taken in moderation to relieve acute back pain, although the side effects can be severe and are underappreciated by prescribing physicians. Taking these common medications for even a short period has been associated with an increased risk of acute heart, even in healthy people.
Muscle Relaxants
If mild to moderate back pain doesn’t improve with OTC pain relievers, your doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants, which may make you sleepy and dizzy.
Topical Pain Relievers
Creams and ointments rubbed into the skin nearby the area of pain.
Opioids
These drugs may be used for a short time under close supervision by your doctor. The issues with this class of medication are that they are addictive, studies show that only 23% of patients with chronic pain find them effective and if used in the long-term, result in more pain for sufferers of chronic low back pain.
Antidepressants
Low doses of antidepressants have been shown to relieve some types of chronic back pain.
Cortisone Injections
A cortisone injection helps decrease inflammation at the site of injection, but the pain relief usually lasts less than a few months even if it is useful.
Magnesium
Where there is ongoing muscular spasming and tension as a result of a magnesium deficiency, dietary magnesium supplementation can help restore this imbalance and resolve pain.
7 Physical Therapy Techniques To Reduce Back Pain
Physical therapies are a highly effective approach to both decrease pain and improve recovery rate from back injuries. Physical therapies may include:
1. Heat Packs
Heat packs cause vasodilation of blood vessels leading to an increased flow of oxygen and nutrients to muscles, which stimulates healing of the damaged tissue. Additionally, heat packs stimulate sensory receptors in the skin, which decreases pain perception in the local area.
2. Postural Assessment And Correction

For many types of back pain, a postural imbalance may be causative or contributing to pain. Your healthcare professional can apply a postural assessment to identify areas of imbalance and develop a strategy to correct this imbalance.
3. Core Strengthening Exercises
In cases where there is either an ongoing postural imbalance or only weakness leading to a significant back injury, it is essential to undertake activities to target weakness and increase function/minimise the recurrence of back pain.
4. Muscle Release Techniques
There are various techniques specially developed to release muscular knots or ‘trigger points’(regions in muscle tissue that are contracted and hypersensitive on pressure producing pain). Such methods may include trigger point therapy and Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) among other techniques.
5. Remedial Massage
Remedial massage improves blood flow and circulation, which leads to oxygen and nutrients flowing to injured tissue and stimulates healing of damaged tissue. Additionally, massage can be applied to release tension in the myofascial system (muscles and connective tissues) and improve range of motion/flexibility.
6. Cupping Therapy
Cupping therapy is very similar to ‘massage therapy’ in many respects when it comes to treating back pain as it is a technique involving the mechanical stimulation of the body. It powerfully improves circulation and releases tension by applying pressure. The difference between the two is that cupping involves a negative pressure (vacuum) which may affect tissues up to 10 cm deep inside the body. Cupping can be applied to improve some situations that massage cannot and vice-versa.
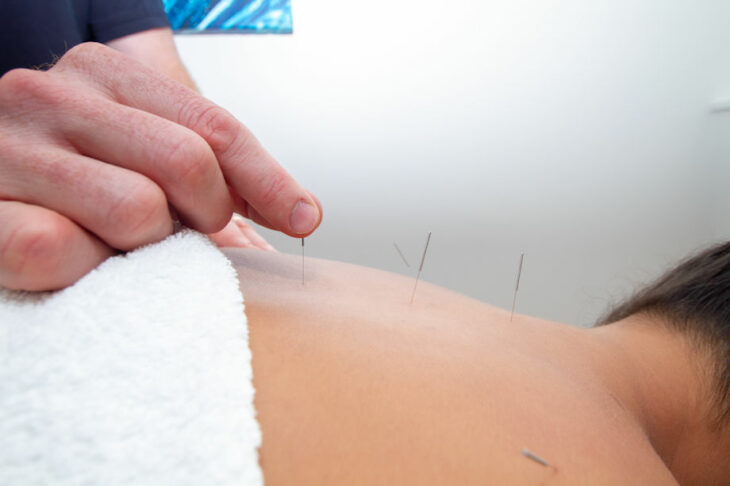
7. Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a highly innovative technology and is the subject of much scientific research. When it comes to back pain, it is known that acupuncture:
- Stimulates the nervous system to deactivate pain centres in the brain
- Stimulates the production of endorphins (the body’s natural painkillers) and improves the brain’s sensitivity to introduced endorphins (opioid medications)
- Regulates several other biochemicals, including ATP (an energy producing compound) and Adenosine which is involved in pain reduction and local tissue healing.
A Comprehensive Approach
It is essential for your healthcare practitioner to listen to concerns/symptoms, diagnose what is the cause of back pain and develop an appropriate treatment plan to achieve a solution to the problem in the least time.
How Is Back Pain Assessed?
Your healthcare practitioner will ask a series of questions, such as:
- When did your back pain start?
- Do you have a history of back pain?
- Is the pain constant or variable?
- What aggravates/improves the pain?
- What types of physical activities do you undertake?
- Do you sleep well?
- Do you take medication?
- What have you tried to improve the pain so far?
Following this, your practitioner will likely undertake some physical assessments and may request diagnostic tests such as X-ray, Ultrasound or blood tests.
Physical therapies are by far the best choice for reducing back pain and avoid adverse effects, which are much more significant with pharmaceutical medications.
With so many different techniques to choose from, it is essential to discuss your goals/health complaint with your health practitioner and ask questions. Only through an experienced practitioner understanding your situation can they apply the best treatment protocol.