Quick Summary
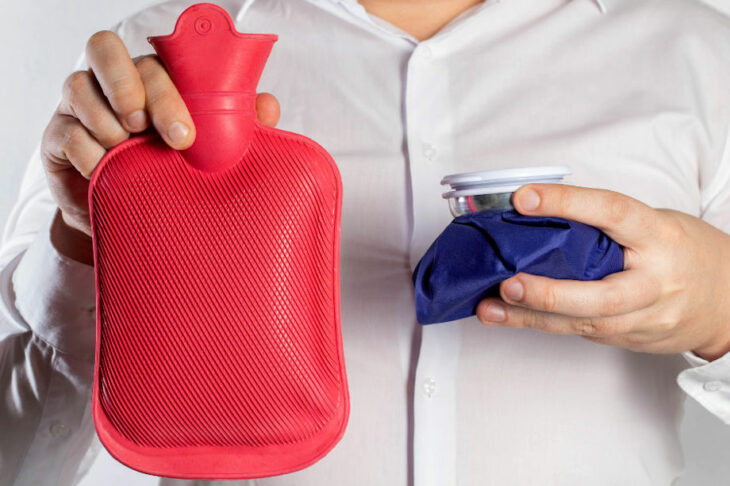
Choosing between heat and cold therapy depends on your condition. Heat therapy promotes vasodilation, increases blood flow, relaxes muscles, and releases endorphins, making it ideal for chronic pain, muscle tension, and arthritis. Cold therapy, on the other hand, induces vasoconstriction, reduces inflammation, and numbs pain signals, making it best for acute injuries, swelling, and post-surgical care.
Both therapies play a role in pain management, but if you’re unsure, personalised treatments like Acupuncture, Remedial Massage, and Cupping Therapy can help restore balance and provide long-term relief.
We’ve all been there—nursing a sore back, dealing with muscle tension, or recovering from an injury. One of the first questions that comes to mind is, “Should I use heat or cold for relief?” It’s a common dilemma, and the answer isn’t always straightforward. The key to effective pain management lies in understanding the science behind each method. By delving into the biochemical mechanisms at play, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your individual situation.
The Science of Pain
Pain is not just a sensation; it’s a complex biochemical process that involves multiple systems in the body. When you experience pain, your nervous system sends signals to your brain, alerting it to the discomfort. This is often accompanied by inflammation, a natural response that involves the release of various hormones and cytokines, proteins that play a vital role in the immune system and the body’s response to inflammation. These biochemical agents work in tandem to either alleviate or exacerbate the pain you’re experiencing.
Before we dive into discussing whether heat or cold will be best for your situation, let’s break down how pain actually manifests:
Inflammation
Inflammation is your body’s immediate response to injury or infection. While it’s essential for the healing process, excessive inflammation can lead to prolonged discomfort. The release of cytokines and other inflammatory markers can aggravate the affected area, making it crucial to manage this aspect effectively.
Nervous System
The nervous system plays a pivotal role in how we perceive pain. It’s the communication network that transmits pain signals from the affected area to the brain. The sympathetic “fight or flight” and parasympathetic “rest & digest” nervous systems also contribute to how your body reacts to pain, influencing factors like blood flow and heart rate.
Hormones
Hormones like cortisol and endorphins also come into play. While cortisol is often associated with stress and can exacerbate pain, endorphins act as natural painkillers. Understanding the hormonal balance is key to effective pain management.
Homeostasis
At the core of these biochemical interactions is the concept of homeostasis—the body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment. When you’re in pain, this balance is disrupted. The aim is to restore homeostasis by modulating factors like blood flow, inflammation and neurotransmitter activity.
Heat Therapy: When and Why
When it comes to alleviating certain types of pain, heat therapy can be incredibly effective. But how does it actually work? Let’s delve into the science behind it.

Vasodilation
One of the primary effects of applying heat is vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels. This process enhances blood flow to the affected area, supplying it with essential nutrients and oxygen. Increased blood flow can accelerate the healing process and relieve muscle tension.
Blood Flow
Improved blood flow is more than just a conduit for nutrients; it also aids in the removal of waste products that can contribute to pain. By enhancing circulation, heat therapy helps flush out substances like lactic acid, which is often associated with muscle soreness.
Endorphins
Heat therapy also stimulates the release of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers. These hormones interact with opioid receptors in the brain to reduce the perception of pain, offering a sense of relief and well-being.
Common Conditions Beneficial for Heat Therapy
- Muscle Tension: Heat relaxes tight muscles, providing relief from tension and spasms.
- Chronic Pain: Conditions like old fractures or traumatic injuries benefit from heat therapy as it improves joint mobility.
- Arthritis: The increased blood flow and relaxation of muscles can ease the stiffness associated with arthritis.
Cold Therapy: When and Why
While heat therapy is excellent for certain conditions, cold therapy has its own set of advantages, particularly for acute injuries. Let’s explore why cold therapy is so effective.

Vasoconstriction
The opposite of vasodilation, vasoconstriction narrows the blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the affected area. This helps to minimise swelling and inflammation, two factors that can exacerbate pain.
Reduced Inflammation
Cold therapy is particularly effective in reducing inflammation. By lowering the temperature of the affected area, it inhibits the release of inflammatory markers like cytokines and prostaglandins.
Nervous System Modulation
Cold therapy also modulates the nervous system by numbing the affected area. This slows down nerve impulses, reducing the frequency of pain signals sent to the brain.
Common Conditions Beneficial for Cold Therapy
- Acute Injuries: Sprains, strains, and other sudden injuries benefit from the immediate application of cold to reduce swelling.
- Swelling: Cold therapy is effective in reducing swelling post-surgery or after an acute injury.
- Post-Surgical Care: Cold compresses can help manage pain and inflammation after surgical procedures.
Both heat and cold therapies have their unique mechanisms of action. Knowing when to use each can make a significant difference in your pain management strategy.
Heat vs Cold: A Comparative Overview
Understanding the science behind heat and cold therapy is crucial, but how do you decide which is best for your specific condition? Let’s summarise the key differences to help you make an informed choice.

Mechanisms
- Heat Therapy: Promotes vasodilation, increases blood flow, and stimulates the release of endorphins.
- Cold Therapy: Induces vasoconstriction, reduces inflammation, and modulates the nervous system.
Appropriate Conditions
- Heat Therapy: Generally better for chronic conditions like muscle tension, arthritis, digestive and menstrual discomfort and ongoing pain.
- Cold Therapy: More effective for acute conditions such as sprains, swelling, and post-surgical care.
Precautions
- Heat Therapy: Avoid on fresh injuries, inflamed areas, or where there’s broken skin.
- Cold Therapy: Not recommended for stiff muscles or joints and should be used cautiously on areas with poor circulation.
The Evolution Medical Care Approach
At Evolution Medical Care, we understand that pain is a complex issue requiring a multi-faceted approach. That’s why we offer a range of science-backed treatments designed to address the root cause of your discomfort.

Neurotransmitters
Treatments like Acupuncture have been shown to modulate neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers that transmit signals in the nervous system. This can help in reducing the perception of pain and improve your overall sense of well-being.
Cortisol Levels
Stress can exacerbate many health conditions, including chronic pain. Our Remedial Massage Therapy aims to reduce cortisol levels, helping you to relax and potentially lowering your sensitivity to pain.
Inflammation
Inflammation is often a key player in pain, and our Cupping Therapy can be an effective way to manage it. By creating suction on the skin, cupping can stimulate blood flow and may help in reducing inflammation.
Our holistic approach integrates these treatments into a personalised pain management strategy, designed to restore your body’s natural state of homeostasis. Whether it’s through heat, cold, or other science-backed treatments, our goal is to provide you with the most effective, individualised care possible.
Conclusion
Pain is a complex experience that involves intricate biochemical interactions within our bodies. From the nervous system sending signals to our brain, to the hormones and cytokines that influence these signals, understanding this science is crucial for effective pain management. Whether it’s heat therapy’s ability to increase blood flow and release endorphins, or cold therapy’s effectiveness in reducing inflammation and modulating the nervous system, each has its unique benefits and precautions.
The choice between heat and cold therapy isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer but depends on your specific condition and individual needs. By understanding the underlying mechanisms, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your health goals.
If you’re still unsure about which therapy is right for you, we’re here to help. At Evolution Medical Care, we’re passionate about providing science-backed, individualised care that addresses the root cause of your pain. Book an appointment online or give us a call at (02) 4709 6727. We look forward to discussing how we can assist you in your journey towards better health.